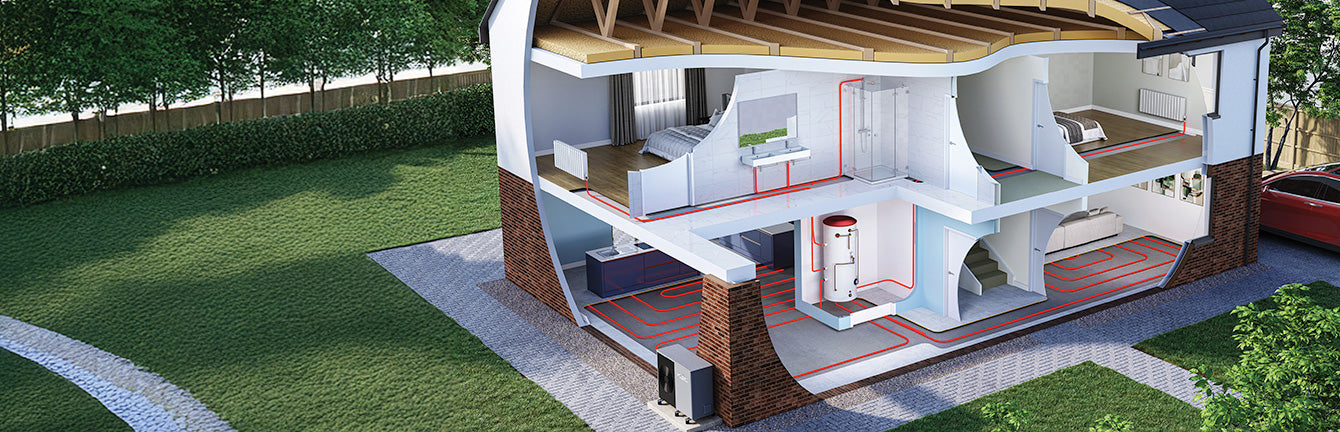
The Basics of Air Source Heat Pumps
An air source heat pump is a renewable energy system that extracts heat from the outside air and uses it to heat your home or provide hot water. Yes, even when it’s cold outside! They rely on advanced technology to capture and transfer heat efficiently, offering a greener alternative to traditional heating systems like gas or oil boilers.
How They Work: Step-by-Step
-
Heat Absorption from the Air
The process begins with the outdoor unit of the ASHP, which contains a heat exchanger. This unit absorbs heat from the air outside, even when temperatures are as low as -20°C. A refrigerant, a special fluid with a low boiling point, flows through the heat exchanger and absorbs this heat. -
Heat Boosting (Compression)
The refrigerant, now warmed, passes into a compressor. The compressor increases the refrigerant’s pressure, which raises its temperature significantly. This is where the "magic" of the heat pump happens — it transforms low-grade heat from the air into usable heat for your home. -
Heat Transfer to Your Home
The hot refrigerant flows into a second heat exchanger, transferring its heat to your home’s heating system. This energy can be used to warm radiators, underfloor heating, or a hot water cylinder. -
Recycling the Refrigerant
After the heat is transferred, the refrigerant cools down and returns to its original state. It flows back to the outdoor unit to start the process all over again.
Efficiency and Benefits
Air source heat pumps are incredibly efficient. For every unit of electricity used to power the system, an ASHP can produce three to four units of heat. This efficiency makes them a cost-effective option for many homeowners, especially when paired with renewable energy incentives or low-carbon electricity sources.